API Guide
With SoundCloud API you can build applications that take music to the next level. With this guide we explain and provide code examples for a lot of common integration use cases like playing and uploading tracks, liking a playlist or discovering new music. If you're looking for more in depth information, feel free to jump to our API Explorer.
Now go ahead and jump to the section you're most interested in and get started.
- Sign in with SoundCloud
- Authorization Code Flow
- Client Credentials Token Exchange Flow
- Refreshing Tokens
- Mobile and Desktop Applications
- Signing Out
- Accessing Resources
- Getting Information about Authenticated User
- Uploading Audio Files
- Updating Metadata
- Creating Playlists
- Adding Tracks to a Playlist
- Accessing Playlists
Authentication
Uploading Tracks
Playing Tracks
Follow & Like
Search
Pagination
SoundCloud URLs
Cross Domain Requests
Errors
Authentication
This documentation will guide you through integrating your application with SoundCloud using OAuth 2.1.
This section presumes you have:
- Registered your App
-
You have obtained your API credentials (
client_idandclient_secret).
In order to integrate with Soundcloud you need to authorize your application. SoundCloud authentication uses the OAuth 2.1 draft, a popular open standard used by many API providers. OAuth 2.1 allows users to authorize the application without disclosing their username and password.
If you have already implemented authorization using OAuth2.0, you can see the differences between these standards in the RFC.
PKCE is now required in order to securely exchange the auth code.
There are different ways to authenticate with OAuth, depending on the needs of an application you're building.
Supported Authorization flows:
- Authorization Code: Your application intends to perform actions on a user's behalf (track upload) as well as access user's data (their account, including any private tracks or playlists that they have created or that have been shared with them). In that case your app has to get permission from Soundcloud, and the user, to access SoundCloud on their behalf.
- Client Credentials: Your application intends to access public resources only. That implies searching for a track, or a playlist, playback and URL resolution. For these purposes you do not require a user session, just an authorized app.
In further sections you can find more detailed information about each of the authentication methods.
| Flow | User Resources Access | Server-side Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization Code | Yes | Yes |
| Client Credentials | No | Yes |
In this section:
Sign in with SoundCloud
You can simplify your registration and sign in process by using a Connect with SoundCloud button. This lets your user know that they can register for your app with one click using their SoundCloud account. It also grants your app access to their account and gives you the ability to upload tracks, create playlists and otherwise act on their behalf.









Authorization Code Flow
1. Redirect User to Authorization URL
Your application should construct the authorization URL with the necessary parameters and then redirect the user's browser to this URL. This step must be performed on the front-end of your application, as it involves user interaction.
# authenticate your app through SC Connect
# open in the browser
$ https://secure.soundcloud.com/authorize \
?client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID \
&redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI \
&response_type=code \
&code_challenge=CODE_CHALLENGE \
&code_challenge_method=S256 \
&state=STATE
YOUR_CLIENT_ID: The client ID you obtained during application registration.
YOUR_REDIRECT_URI: The URI you provided during application registration. After authentication,
the user will be redirected to this URI.
Your application should be prepared to receive and process the authorization code at this URI.
CODE_CHALLENGE: A PKCE code challenge. You can read about it
here and use this
PKCE generator sandbox to understand how it works.
STATE: A random string to protect against CSRF attacks.
Security Advice
Use the state parameter for
CSRF protection. Pass a sufficient random nonce here and verify this nonce again
after retrieving the token.
2. User Authorization
A pop-up window will be opened allowing the user to log in to SoundCloud and approve your app's authorization request. If the user is already signed into SoundCloud, they will be able to authorize your request in one click.
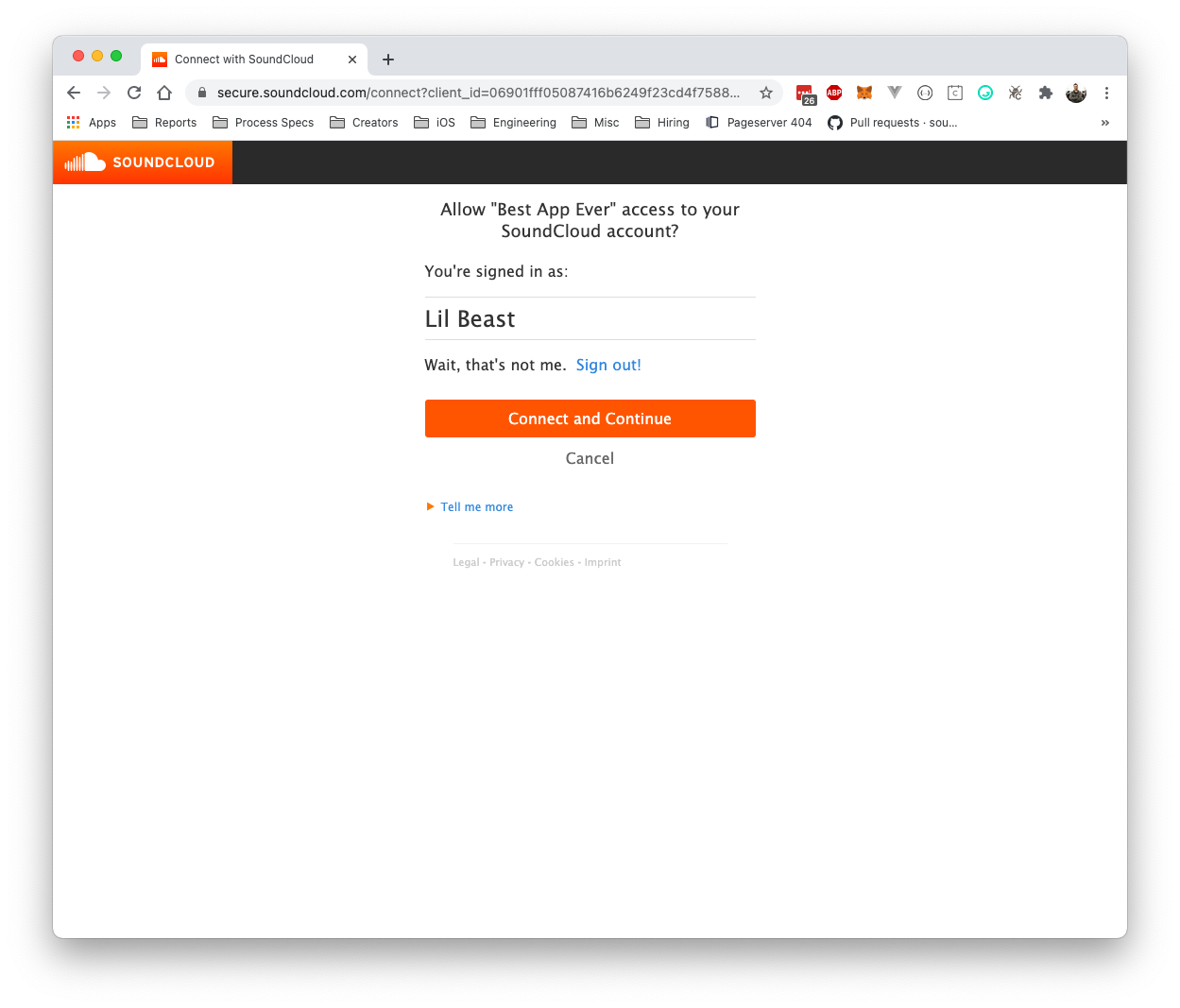
3. Obtain Access Token
If the user approves your authorization request, they will be sent
to the redirect_uri you specified when registering your app. Your application
should extract the code parameter from the query string and use it to obtain an access token.
# obtain the access token
$ curl -X POST "https://secure.soundcloud.com/oauth/token" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=authorization_code" \
--data-urlencode "client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \
--data-urlencode "client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET" \
--data-urlencode "redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI" \
--data-urlencode "code_verifier=YOUR_PKCE_GENERATED_CODE_VERIFIER" \
--data-urlencode "code=YOUR_CODE"
YOUR_CLIENT_ID, YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET: obtained during application registration.
YOUR_PKCE_GENERATED_CODE_VERIFIER: generated by your application during step 1.
YOUR_REDIRECT_URI: the same redirect URI you used in the authorization request. This must match exactly to ensure security.
YOUR_CODE: the authorization code your application received from the authorization server.
4. Store and Use Tokens:
The returned object has an access_token property and a refresh_token
property as well as expires_in and scope.
You should now store the object in a database or a data storage of your choice. Associate it
with the user it belongs to and use the access_token from now on instead of
sending the user through the authorization flow on each API interaction.
Use the refresh_token returned in the body to automatically renew the expired token via the refresh token flow.
# make an authenticated call
$ curl "https://api.soundcloud.com/me" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN"Client Credentials Token Exchange Flow
With applications, such as CLIs, or pure back-end services, you would authenticate the application itself
rather than a user. For instance, you might want to build an artist's website where you only need an access
to their tracks, playlists, or user information. There is no need to go through the connect flow, as
SoundCloud API provides the Client Credentials Flow for these purposes. You pass along the
client_id and client_secret you have acquired at registration
to authenticate and get a token.
# obtain the access token
$ curl -X POST "https://secure.soundcloud.com/oauth/token" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-H "Authorization: Basic Base64(client_id:client_secret)" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=client_credentials"
# If your client_id is "my_client_id" and client_secret is "my_client_secret"
# The concatenated string would be "my_client_id:my_client_secret"
# The Base64 encoded string of "my_client_id:my_client_secret" is "bXlfY2xpZW50X2lkOm15X2NsaWVudF9zZWNyZXQ="*** Developers migrating to new endpoints should note that for the client_credential grant type, ONLY basic header client authentication is supported. Client credentials as request content has been dropped.
Similarly to the Authorization Code flow, you receive an object that has an access_token,
refresh_token properties as well as expires_in and scope.
Store the object in a database or a data storage of your choice. Associate it with the user it belongs to
and use the access_token for requesting data from our API. Use the refresh_token to automatically renew the expired
token.
Please be aware there is rate limiting on the amount of tokens you can request through the Client Credentials Flow: 50 tokens in 12h per app, and 30 tokens in 1h per IP address. In order to not hit the limit we highly recommend reusing one token between instances of your service and implementing the Refresh Token flow to renew tokens.
Note: Currently, all clients are treated as confidential rather than public, meaning that a secret is required to obtain a token.
Refreshing Tokens
As the access tokens expire you will need to periodically refresh them. Currently a token lives around 1 hour.
You can set an automatic process that checks the expiration time of a current token and updates it using
the provided refresh_token. Each refresh token can only be used once.
Note: Currently, all clients are treated as confidential rather than public, meaning that a secret is required to obtain a token.
# refresh token
$ curl -X POST "https://secure.soundcloud.com/oauth/token" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=refresh_token" \
--data-urlencode "client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \
--data-urlencode "client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET" \
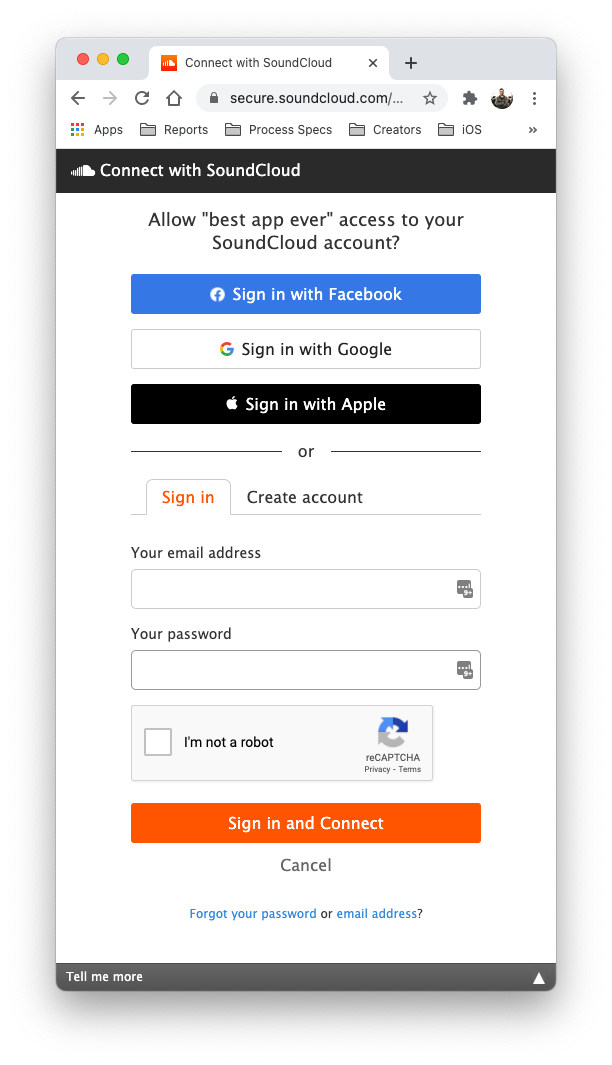
--data-urlencode "refresh_token=YOUR_TOKEN" \Mobile and Desktop Applications
You authenticate mobile and desktop applications the same way you
do for web applications. To make the flow smoother, you
can use a redirect_uri with a custom protocol scheme and set your
app as a handler for that protocol scheme. For example, your
redirect_uri could be something like my-app://soundcloud/callback.
When building apps for mobile devices, we recommend using our
mobile optimized connect screen by setting display=popup
in the authorization URL query string.
Signing Out
To sign out the user, send the access_token as follows:
$ curl -X POST "https://secure.soundcloud.com/sign-out"
# JSON body:
{
"access_token": "the-application-access-token"
}
# Error:
{
"error": "XXXX"
}Error details:
| Response | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bad_request | 400 | body is missing access token |
| unauthorized | 401 | this token is associated with a session that is already invalid |
Accessing Resources
All Soundcloud resources (tracks, playlists, users) can only be accessed by an authenticated applications. That said, every request to our API requires an Authorization header in the following format:
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
Note that requests without the header will be rejected with a 401 Unauthorized error.
Check the Authentication section to learn about
supported auth methods.
Getting Information about the Authenticated User
Once the user has signed into SoundCloud and approved your app's authorization request, you will be able to access their profile and act on their behalf. We have provided a convenient endpoint for accessing information about the authenticated user.
$ curl "https://api.soundcloud.com/me" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"Uploading Tracks
This section presumes you have:
Tracks are core to SoundCloud. Our API gives you the ability to upload, manage and share tracks. Your app can take an audio file and upload it to a user's SoundCloud account. You can also manage metadata (including tags) or add the track to playlists. We support the following formats: AIFF, WAVE, FLAC, OGG, MP2, MP3, AAC, AMR and WMA.
In this section:
Uploading Audio Files
To upload a track, send a POST request with a multipart/form-data
media type to the /tracks
endpoint.
Request bodies for track uploads via the API may not be larger than %strong 500MB.
$ curl -X POST "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" \
-F "track[title]=YOUR_TITLE" \
-F "track[asset_data]=@PATH_TO_A_FILE"If successful, your track will immediately be queued up for encoding.
See also:
- /tracks endpoint reference documentation
- Desktop sharing kits
- iOS sharing kit
- Android sharing kit
Updating Metadata
In order to update a track's metadata, send a PUT request to the
/tracks/:id endpoint,
passing in the path of the track resource and the properties you want to update.
You can update the track artwork using the artwork_data parameter.
Please note that at this time it is not possible to update the actual track audio
file.
For a full list of properties that can be set on a track resource, see the endpoint reference.
# Multipart request
$ curl -X PUT "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/TRACK_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: mmultipart/form-data" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-F "track[title]=YOUR_TITLE" \
-F "track[description]=YOUR_DESCRIPTION" \
-F "track[artwork_data]=PATH_TO_FILE"
# Json request
$ curl -X PUT "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/TRACK_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-d '{"track":{"title":"NEW TITLE"}}'Creating Playlists
Playlists allow you to organize tracks into groups that can be shared together. For example, tracks in an album or in a specific collection can be grouped together using a playlist and then shared to the world. You can add any tracks to a playlist and a track can belong to multiple playlists. Playlists can be either private or public.
You create playlists through our API by sending the POST request to the
/playlists
endpoint and providing the information about the playlist, including a list of track ids.
$ curl -X POST "https://api.soundcloud.com/playlists" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-d "{'playlist': {'title':'YOUR_TITLE', 'description':YOUR_DESCRIPTION, 'sharing':'public', 'tracks':[{'id':1},{'id':2},{'id':3}]}}"Adding Tracks to a Playlist
Once a playlist has been created, you can continue to add tracks to it by
updating the tracks property. You can also update the playlist's metadata.
$ curl -X PUT "https://api.soundcloud.com/playlists/PLAYLIST_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-d "{'playlist': {'tracks':[{'id':1}, {'id':2}, {'id':3}]}}"Accessing Playlists
To get a list of tracks in a playlists, send a GET request to the
/playlists/:id
endpoint with the playlist id.
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/playlists/PLAYLIST_ID?show_tracks=false" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"See also:
- /playlists endpoint reference documentation.
Playing Tracks
This section presumes you have:
Yep, you can also play tracks and playlists from your application. Depending on your needs, you can embed a player widget, or feed a stream url into your own audio player. You can also use our Widget API to control the player and handle events.
In this section:
Embedding a SoundCloud Widget
If you have the URL of a track or a playlist, you can get the embed code and paste it into your website. You can also do this in your application using the oEmbed endpoint. Given a track or playlist URL, you can retrieve all of the information you need to embed a player.
Example SoundCloud Widget
See also:
- Embedded player guide
- Widget API
Streaming Tracks
Note if you are going to stream from our API you need to attribute properly. Make sure you've read our Terms and Attribution Guidelines to make sure you treat our creators content correctly. When using a custom player you must:
- Credit the uploader as the creator of the track
- Credit SoundCloud as the source by including one of the logos found here
- Link to the SoundCloud URL containing the work
- If the track is private link to the profile of the creator
If you don't want to use the SoundCloud widget, our API gives you
the ability to access a track's stream URL and use your own player
to play tracks from SoundCloud. In order to get a URL for streaming,
you can request the appropriate resource and make note of
the stream_url property. Send a GET request to that URL and
you will get a set of links with available transcodings which you can choose from.
Note that as long as the track is public, you can access it with no user associated.
If you would like to access the stream URL for a private track, you'll need to
have an authorized user session and a secret_token provided.
# request a track you want to stream
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/TRACK_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
# extract stream_url when available from a response
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/TRACK_ID/stream" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"See also:
- /oembed endpoint reference documentation.
- HTML5 Widget API.
- /tracks endpoint reference documentation.
Restricted Access
Not every track is allowed for streaming off platform. A user might restrict a playback, or
a track might be behind a paywall, geo-blocked and so on. In that case a track in response wont have a
stream_url available and a field access will have blocked. If you
try to call /tracks/:id/streams endpoint you will get an error.
Soundcloud API provides 3 levels of track's access:
playable- a track is fully streamable.preview- a track's preview is available.blocked- a track is not streamable, only metadata is provided.
You can also specify the access when searching or fetching tracks to, for instance,
avoid showing non-streamable tracks. Our endpoints provide a filter
access that accepts an inclusive list of values.
For detailed information check the API Explorer.
Comments
This section presumes you have:
SoundCloud has many social features that make it easier to collaborate, share and get feedback. The primary way that SoundCloud users interact is by leaving comments on each other's tracks.
Our API allows you to leave comments on tracks by calling the
POST method with the
/tracks/:track_id/comments
path and information about the comment. Include the timestamp to make it a timed comment.
Note that you cannot leave comments on tracks if the creator has disabled comments.
$ curl -X POST "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/YOUR_TRACK_ID/comments" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-d "{'comment':{'body':'YOUR_COMMENT'}}"Note that the timestamp value is in milliseconds and represents the amount of time from the beginning of the track. If you omit the timestamp, the comment will be a non-timed one.
You can also get a list of comments for a specified track.
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks/YOUR_TRACK_ID/comments?limit=3&linked_partitioning=true" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"See also:
- /tracks endpoint reference documentation.
Follow & Like
This section presumes you have:
Your application can take advantage of SoundCloud's social features by allowing users to follow other users and like tracks or playlists. Following and liking allows SoundCloud users to customize their experience. Tracks created and reposted by people your user follows will be available in their activity feed.
You can follow a user using the /me/followings/:user_id endpoint.
$ curl -X PUT "https://api.soundcloud.com/me/followings/USER_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"Liking a track or playlist is done using the /likes/ endpoints.
# liking a track
$ curl -X POST "https://api.soundcloud.com/likes/tracks/TRACK_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
# liking a playlist
$ curl -X POST "https://api.soundcloud.com/likes/playlists/PLAYLIST_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"See also:
- /me endpoint reference documentation
- /likes endpoints reference documentation
Search
This section presumes you have:
Resources such as tracks, users, playlists can be searched
using our API. Most endpoints will accept a q param which you can
use to specify a keyword to search for in fields like title,
username, description, etc. depending on the resource type.
# search pnly for playable tracks
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks?q=hello&ids=1,2,3&genres=Pop,House&access=playable&limit=3&linked_partitioning=true" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
You can also specify ranges for bpm, duration, and more.
# search pnly for playable tracks
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks?q=hello&ids=1,2,3&genres=Pop,House&bpm%5Bfrom%5D=120&duration%5Bfrom%5D=30000&access=playable&limit=3&linked_partitioning=true" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"For a complete list of search fields and filters, please check the /search section for the resource type you'd like to search.
Pagination
This section presumes you have:
Most results from our API are returned as a collection. The number
of items in the collection returned is limited to 50 by
default with a maximum value of 200. Most endpoints support a
linked_partitioning parameter that allows you to page
through collections. When this parameter is passed, the response will
contain a next_href property if there are additional results.
To fetch the next page of results, simply follow that URI. If the response
does not contain a next_href property, you have reached the
end of the results.
# fetch first 25 user's playlists
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/me/playlists?show_tracks=false&linked_partitioning=true&limit=25" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
# response contains 'next_href': "https://api.soundcloud.com/playlists?show_tracks=false&page_size=25&cursor=1234567"SoundCloud URLs
This section presumes you have:
If you have a permalink URL to a particular resource, but need more information such as an ID or other property, you can use the /resolve endpoint to extract a full representation of the resource.
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/resolve?url=https://soundcloud.com/PERMALINK" \
-H "accept: */*" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"See also:
- /resolve endpoint reference documentation.
Cross Domain Requests
This section presumes you have:
Our API supports CORS for making cross domain requests. This means you can access SoundCloud API endpoints from JavaScript running in the browser. By requesting results formatted as JSON, you will be able to parse and use the response immediately.
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.7.2.js"></script>
<script>
var url = 'https://api.soundcloud.com/tracks';
$.getJSON(url, function(tracks) {
$(tracks).each(function(track) {
console.log(track.title);
}
});
</script>
We also support JSONP, which can be used by passing a callback
parameter in the query string of the URL you are requesting.
Errors
This section presumes you have:
When an error occurs, our API will return an appropriate HTTP status code and an error message description.
In this section:
# try fetching a non-existing user
$ curl -X GET "https://api.soundcloud.com/users/INVALID_ID" \
-H "accept: application/json; charset=utf-8" \
-H "Authorization: OAuth ACCESS_TOKEN"
# response 404 Error: Not Found
{
"code": 404,
"message": "404 - Not Found",
"link": "https://developers.soundcloud.com/docs/api/explorer/open-api",
"status": "404 - Not Found",
"errors": [
{
"error_message": "404 - Not Found"
}
],
"error": null
}HTTP Status Codes
The response from SoundCloud will have an HTTP status code that will help you determine the cause of the error. Our API tries to use the appropriate HTTP status code to indicate the type of problem encountered.
Below is an overview of what those codes mean, along with some suggestions that might help you fix things.
400 Bad Request
This is likely to be caused by a programming error on your part. Check the requirements of the endpoint you're calling in the API Explorer.
401 Unauthorized
This means that we were not able to authenticate you based on the information provided in the request.
Make sure you're sending an Authorization header.
Our public endpoints will work with an access token acquired through the Client Credentials flow. Acting on behalf of another user is different. The Authentication section gives a detailed explanation of how this works.
If you're connecting using OAuth, don't forget that tokens can expire. These will need to be refreshed. Not doing so can also result in getting a 401 error.
If you need to check your application's details, use the
Your Applications page.
This will include the client_id for your application.
403 Forbidden
You don't have access to whatever it is you're asking for.
404 Not Found
You're asking for something that doesn't exist. Check the URL that you're requesting.
406 Not Accessible
This means it wasn't possible to respond with the format you requested.
Check the Accept header that you're sending.
422 Unprocessable Entity
The request was valid, but one or more of the parameters looks a little screwy. It's possible that you sent data in the wrong format. One example would be providing an array when we expected a string.
429 Too Many Requests
To keep the amount of spam on SoundCloud as low as possible, our API limits the rate at which you can perform certain actions. Read the Rate Limits page to find out more.
500 Internal Server Error
Uh-oh. Something went wrong on our side. We're sorry. We keep track of these, and we'll try to fix it!
503 Service Unavailable
This means that we're having some trouble, and our servers are too busy to handle your request. You'll want to check for these and give your user a chance to retry the request. We keep track of these and try to make sure they don't happen.
504 Gateway Timeout
This means the request is taking too long. However, it doesn't always mean that we didn't receive your request. We could still be chugging away on the changes you made, and this means that you may want to check before retrying.